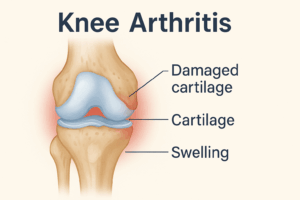
What Is Knee Arthritis?
Knee arthritis most commonly refers to osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease caused by cartilage deterioration. Another form, rheumatoid arthritis, is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks its own joints. Both conditions can severely impact mobility and quality of life if left untreated.
Key Symptoms to Watch For
-
Aching or sharp pain in the knee during or after activity
-
Morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes
-
Swollen or tender knees
-
Popping, cracking sounds, or reduced range of motion
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of knee arthritis:
-
Aging: Cartilage naturally wears down with age.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight increases pressure on the knees.
-
Injuries: Prior trauma or surgery can lead to joint damage.
-
Genetics: A family history of arthritis raises your risk.
-
Repetitive stress: Occupations or sports that strain the knees increase vulnerability.
Proven Treatments for Knee Arthritis
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting certain habits can help control symptoms:
-
Exercise Regularly: Engage in low-impact activities like yoga, walking, or aquatic therapy to strengthen the muscles supporting the knee.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing even 5–10% of your body weight can significantly relieve pressure on your joints.
-
Use Supportive Devices: Braces, orthotic inserts, or canes can provide added support.
Medical Treatments
-
Medications: NSAIDs like ibuprofen can reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Corticosteroid injections may be used for flare-ups.
-
Physical Therapy: A trained physical therapist can develop a personalized plan to improve strength, flexibility, and balance.
Advanced Interventions
-
Viscosupplementation: Involves injecting lubricating fluid into the joint.
-
Surgery: Options include arthroscopy, partial knee replacement, or total knee replacement in advanced cases.
Practical Tips for Daily Life
-
Use ice packs for 20 minutes post-activity to reduce inflammation.
-
Try heating pads in the morning to ease joint stiffness.
-
Avoid high-impact exercises that strain the knees, such as running or jumping.
When to See a Specialist
Consult a doctor if your symptoms persist for more than a few weeks, worsen over time, or severely interfere with daily tasks. Early diagnosis can slow disease progression and improve long-term outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Living with knee arthritis can be challenging, but with proper care, you can take control of your condition. From exercise and weight management to advanced therapies and surgical solutions, there are many ways to reduce pain and improve mobility. Always consult with a healthcare provider to find the treatment plan that works best for your needs.